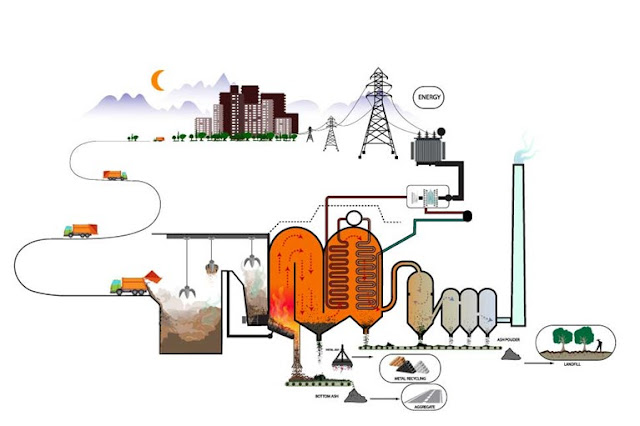
Comparison between waste to energy and landfill to energy
Waste-to-energy (WTE) and landfills both have impacts. WTE is a controlled process that reduces greenhouse gases (GHG) and recovers valuable resources. Landfills releases harmful chemicals that can be controlled by various technologies to produce renewable resources.
Both WTE and landfills are critical aspects of environmental conservation and sustainability. Each approach has its advantages and disadvantages, which should be considered when making decisions about how to manage waste.
Waste-to-energy
Advantages:
- Energy Generation: WTE facilities can produce electricity and heat, contributing to the local energy supply.
- Reduces Land Use: WTE facilities typically require less land compared to landfills.
- Lower Greenhouse Gas Emissions: While not emission-free, WTE can reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to Methane from landfills.
- Waste Reduction: It helps to reduce the volume of waste that ultimately ends up in landfills.
- Reduces fossil fuel use: WTE facilities reduce the need for coal and natural gas.
- Operates 24/7: WTE facilities operate 24/7 to reduce baseload fossil-fuel generation.
- Located in populated areas: WTE facilities are located in populated areas where power is needed the most.
- Air Emissions: WTE can release pollutants like particulate matter and greenhouse gases into the air, which may require strict emission control measures.
- High Initial Costs: Establishing and maintaining WTE facilities can be very expensive with high capital investment due to specialized equipment, operating, and maintenance costs.
- Limited Recycling Incentive: WTE facilities can destroy recoverable materials, which can reduce motivation to recycle when waste can be burned for energy.
- Health Concerns: Incineration produces dioxin (PM2.5 and PM10 can be inhaled into the lungs and can induce adverse health effects such as cardiovascular effects such as cardiac arrhythmias and heart attacks Respiratory effects such as asthma attacks and bronchitis) due to potential emissions, although modern facilities are subject to rigorous regulations.
Landfills
The following listed the advantages and disadvantage of disposing trash at a landfill in a controlled manner. However, Methane (landfill gas) produced from landfills, even though a harmful greenhouse gas (GHG), can be beneficial if managed properly to produce renewable energy sources. See Landfill Gas to Renewable Energy for more information.
Advantages:
- Lower Initial Costs: Landfills are typically less expensive to establish and operate compared to WTE facilities.
- Land Reclamation: Some landfills can be repurposed for other uses after closure.
- Simple Technology: Landfills require less complex technology and can be managed with relatively simple infrastructure.
- Landfills Are an Excellent Energy Source: Carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4) are produced when trash accumulates and begins to break down. These gases can be taken out, filtered, and used to produce energy.
- Space Limitations: Land is a finite resource, and finding suitable landfill sites is becoming increasingly challenging.
- Environmental Impact: Landfills can leach harmful chemicals into the groundwater and emit Methane, a potent greenhouse gas.
- Long-Term Maintenance: Landfills require monitoring and maintenance for years or even decades after closure.
- NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) Opposition: Communities often resist the establishment of new landfills due to concerns about odor, noise, and environmental impact.
In summary:
The choice between waste-to-energy and landfill disposal depends on various factors, including local regulations, environmental priorities, and available resources. Many regions use a combination of both methods to address their waste management needs. Sustainable waste management solutions are increasingly focusing on reducing waste generation, increasing recycling rates, and exploring alternative technologies to minimize the environmental impact of waste disposal.
Comments
Post a Comment