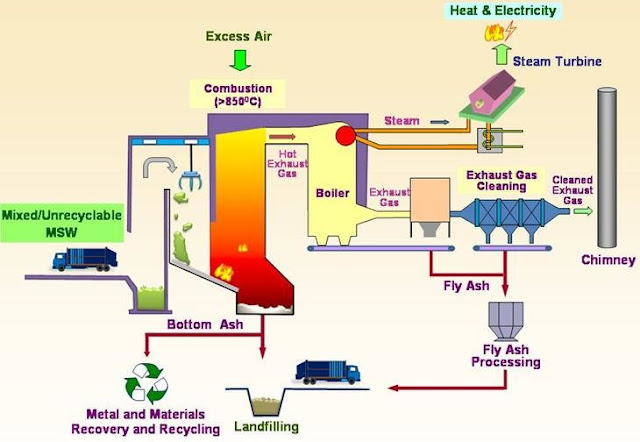
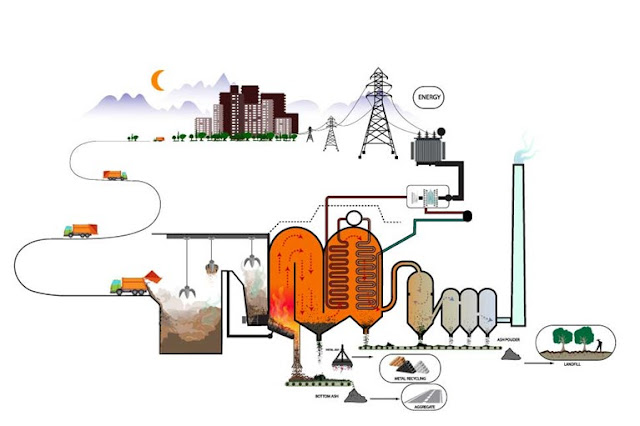
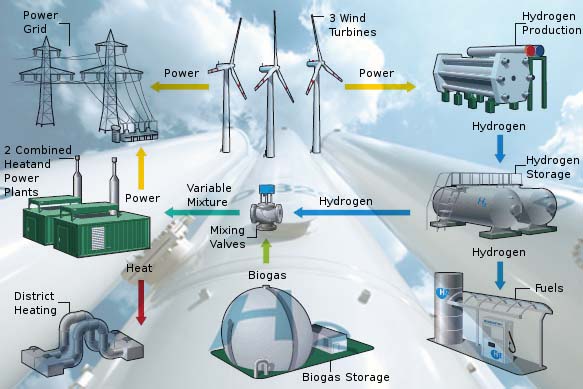
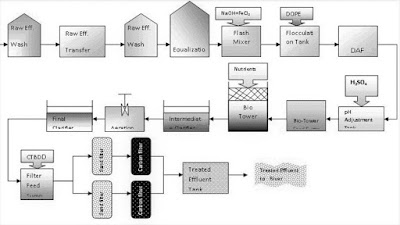
Landfill Gas to Renewable Energy
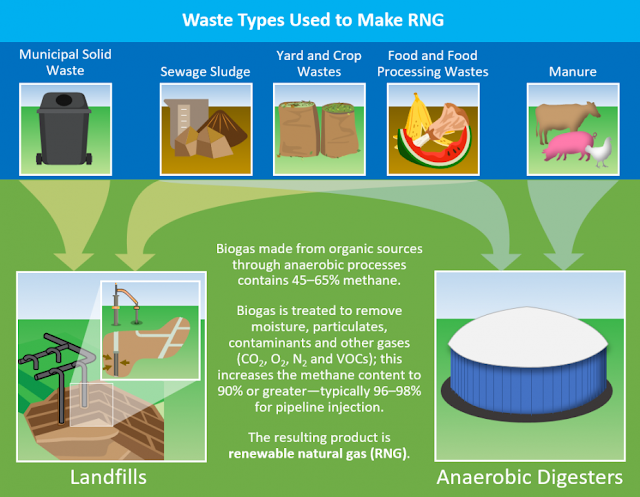
Landfill gas (LFG) is a natural byproduct of the decomposition of organic waste in landfills. It consists of methane, carbon dioxide, and other organic compounds. Methane (CH4) is a significant component of LFG that is more than 25 times as potent as carbon dioxide (CO2) at trapping heat in the atmosphere. Methane is a potent greenhouse gas (GHG) and a significant contributor to global warming. While LFG can be harmful to the environment, it can also be harnessed as a valuable source of renewable energy. Many landfills collect and treat LFG to generate electricity or heat while reducing environmental impact. Landfill gas to energy (LFGTE) - Landfill gas to energy is a process that involves capturing and converting the methane gas produced by the decomposition of organic waste in landfills into usable energy, typically electricity or heat or producing renewable natural gas (RNG). LFGTE projects not only help reduce the emission of methane, but they also provide a source of renewable ene...